

Reports the identification of the first known mediator of mitochondrial fusion and, at the same time, describes the role of fusion in remodelling of mitochondria during spermatogenesis. Developmentally regulated mitochondrial fusion mediated by a conserved, novel, predicted GTPase. Mechanisms of membrane fusion: disparate players and common principles. Mitochondrial morphology and dynamics in yeast and multicellular eukaryotes. The machines that divide and fuse mitochondria.
Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics. Mitochondria are morphologically and functionally heterogeneous within cells.

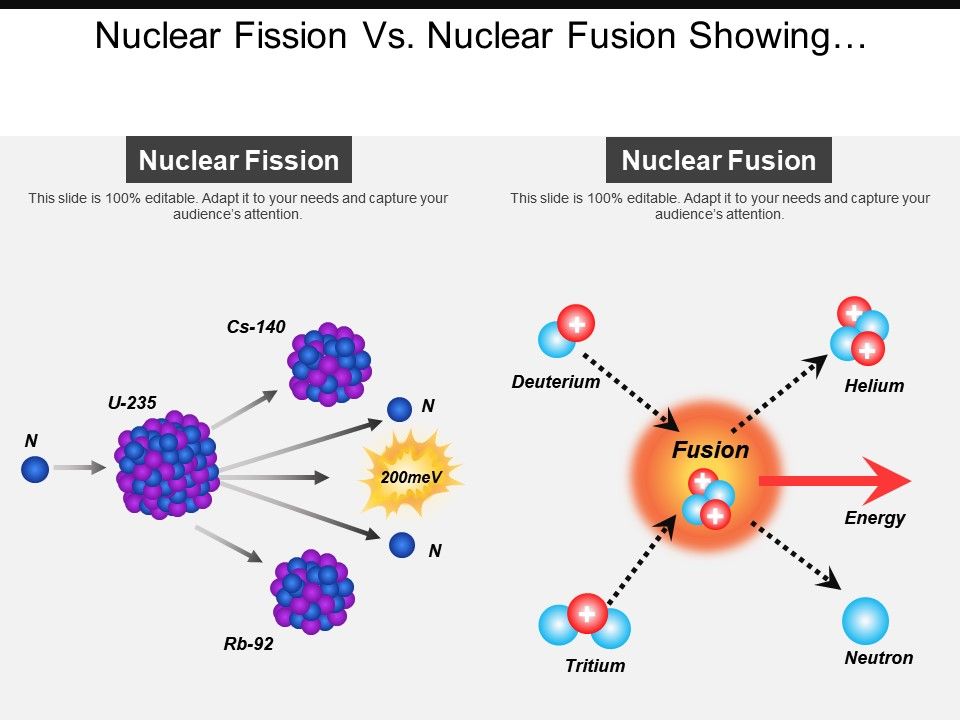
Mitochondrial filaments and clusters as intracellular power-transmitting cables. Behavior of mitochondria in the living cell. An electron microscope study of the mitochondrial structure. Furthermore, mitochondrial division is an important step in apoptosis.ĭysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics contribute to several inherited and age-associated neurodegenerative diseases. Mitochondrial dynamics counteracts cellular ageing by allowing complementation of gene products after fusion of impaired mitochondria, and it constitutes an important part of organellar quality control as it facilitates the elimination of damaged mitochondria by autophagy. Mitochondrial fusion and fission are required for faithful inheritance and proper intracellular distribution of the organelle. The machineries of mitochondrial fusion and fission are regulated by many cellular pathways, including proteolytic processing, ubiquitylation, sumoylation, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Only little is known about division of the inner membrane. Mitochondrial fission is mediated by dynamin-related proteins (DRPs) and cofactors that are required for assembly of DRP rings and spirals on the mitochondrial surface. Two evolutionarily conserved large GTPases constitute the core machinery of fusion: mitofusins are found in the outer membrane, and Mgm1 and optic atrophy protein 1 (OPA1) are found in the inner membrane of yeast and mammals, respectively. 36, 844–863.Live cell imaging studies showed that mitochondria are highly dynamic organelles that frequently fuse and divide. Clinical studies focusing on acute ( i.e., myocardial infarction) and chronic ( i.e., heart failure) cardiac diseases are needed to validate the effectiveness of such strategies in improving mitochondrial morphology, metabolism, and cardiac function.
The current and future challenges are turning these lead molecules into treatments. Recent Advances: Disruption of quality control systems that maintain mitochondrial number, size, and shape through fission/fusion balance and mitophagy results in dysfunctional mitochondria, defective mitochondrial segregation, impaired cardiac bioenergetics, and excessive oxidative stress.Ĭritical Issues: Pharmacological tools that improve the cardiac pool of healthy mitochondria through inhibition of excessive mitochondrial fission, boosting mitochondrial fusion, or increasing the clearance of damaged mitochondria have emerged as promising approaches to improve the prognosis of heart diseases.įuture Directions: There is a reasonable amount of preclinical evidence supporting the effectiveness of molecules targeting mitochondrial fission and fusion to treat cardiac diseases. Accumulation of fragmented and damaged mitochondria is a hallmark of cardiac diseases. Significance: Mitochondria play a critical role in the physiology of the heart by controlling cardiac metabolism, function, and remodeling.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
